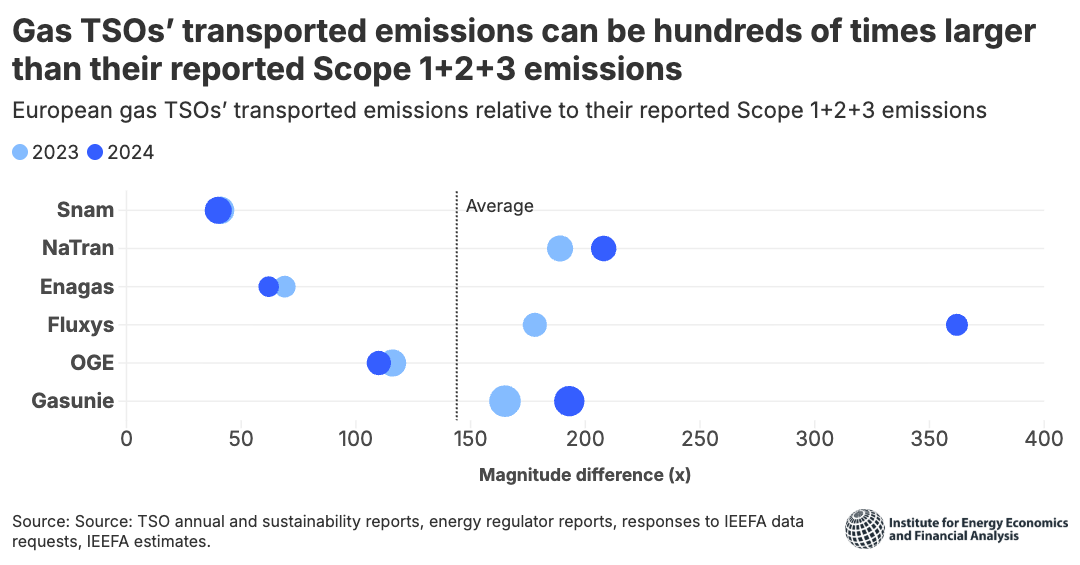
European gas pipeline companies report less than 1% of their emissions
Key Takeaways:
European gas pipeline companies refuse to report downstream emissions from the gas they transport, which average 150 times larger than the emissions they do report.
Their reporting practice keeps these “transported emissions” off the books, creating potential for greenwashing and unpriced risk at the financial institutions that lend to and invest in them.
This loophole has formed primarily because of a lack of clear guidance from standard-setter the Greenhouse Gas Protocol.
Closing this loophole could add significant credibility to gas pipeline companies’ transition plans, financing frameworks and business strategies.
22 December 2025 (IEEFA) | European gas pipeline companies, known officially as transmission system operators (TSOs), report less than 1% of their emissions on average because of a climate accounting loophole that lets them obscure their environmental impact from investors.
New research from the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) finds that a lack of guidance from standard-setter the Greenhouse Gas Protocol allows pipeline companies to not report emissions from the final use of gas they transport.
This “transported emissions” ambiguity means that investors may gain the false impression that these gas TSOs are low-carbon entities which are somehow separate from the fossil fuel value chain and its risks — when in fact they are its crucial “midstream” link.
This creates potential for greenwashing and unpriced risk at the financial institutions that serve these gas pipeline companies, as these indirect emissions effectively remain off the books.
“This fundamental flaw in climate accounting distorts the market by enabling gas pipeline companies to attract capital that might otherwise flow to greener investments,” said Arjun Flora, energy finance analyst at IEEFA and author of the report.
“The broader risk is that this loophole ultimately delays the electrification of gas-consuming sectors and the transition away from fossil fuels.”
The report covers six European gas pipeline companies, none of which report transported emissions: Enagás, Fluxys, Gasunie, NaTran, Open Grid Europe and Snam. Collectively they own and operate over 100,000km of gas pipelines and more than half of the EU’s liquified natural gas terminals.
IEEFA estimates these six companies’ total transported emissions to be 700 million tonnes of carbon dioxide annually — similar to the greenhouse gas emissions of Germany, the EU’s largest economy.
These companies’ transported emissions are on average about 150 times larger than their total reported emissions.
The TSOs cite the technicality that they do not own or sell the gas as justification for not reporting transported emissions.
“This contradicts gas pipeline companies’ marketed role as energy transition partners committed to reducing emissions by shifting to low-carbon gas networks. They are not merely neutral transporters of third-party gas, but powerful corporate actors that actively shape European energy policy,” said Flora.
“It follows logically that these companies should fully recognise downstream emissions from the gas they transport in their Scope 3 emissions. That they do not — despite clear guidance from disclosure experts CDP and target-certifier the Science Based Targets initiative — should give stakeholders cause for concern.”
The report finds that there has so far been insufficient pressure on gas pipeline companies to improve their transparency.
This is partly because of contradicting advice from the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, as well as the delay of sector-specific European Sustainability Reporting Standards.
In IEEFA’s view, closing the transported emissions loophole would enable gas pipeline companies to demonstrate their progress, as they work towards realising their shared vision of a low-carbon gas network supporting Europe’s energy security.
Flora said: “Reporting these emissions would add significant credibility to gas pipeline companies’ transition plans, financing frameworks and business strategies when communicated to financial markets, regulators and the public.”
Notes to editors
- Gas TSOs own and operate the high-pressure pipeline networks, liquefied natural gas terminals and gas storage assets that form the backbone of Europe's natural gas supply. These companies link gas producers and importers with distributors and major consumers, such as gas power plants or large industrial users. The gas that TSOs transport accounts for about 29% of Europe’s annual fuel combustion emissions, according to the International Energy Agency.
- Scope 3 emissions are indirect emissions (not included in Scope 2) that occur in the value chain of a reporting company, including both upstream and downstream emissions. European TSOs exclude the downstream emissions from the gas they transport from their Scope 3 reporting, citing the technicality that they do not own or sell the gas.
- “Total reported emissions” refers to total direct (Scope 1) and indirect (Scope 2 and Scope 3) greenhouse gas emissions, as defined by the Greenhouse Gas Protocol.
- Over the last decade, European gas TSOs have rebranded themselves as energy transition partners and have actively promoted low-carbon gases. This is despite the lack of scalable markets or supply chains for these low-carbon gases, mainly because they are too expensive, too inefficient or too experimental for their proposed applications. TSOs advocate for supportive policies through groups such as the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Gas (ENTSO-G), Gas Infrastructure Europe, the European Hydrogen Backbone initiative, Gas for Climate and CCS Europe.
Read the report: https://ieefa.org/resources/pipelines-uncertainty-need-full-emissions-transparency-europes-midstream-gas-sector
Press contact
Jules Scully | [email protected] | +447594 920255
About IEEFA
The Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) examines issues related to energy markets, trends and policies. The Institute’s mission is to accelerate the transition to a diverse, sustainable and profitable energy economy. www.ieefa.org