IEEFA: Repurposing coal plants into solar and battery can pay up to 5 times more than decommissioning
Worldwide, coal plants are grappling with environmental issues and low capacity utilization levels. They have not only become unprofitable to utilities, they are also uneconomical to customers.
While retiring end-of-life coal plants can overall be very beneficial, and indeed necessary as finance continues to exit the fossil fuel sector driven by the global energy transition, the execution may encounter resistance for several reasons such as costs involved, identification of plants, impact on the existing workforce and hence communities, and other system flexibility considerations.
We suggest retirements can be better rationalized with a clear empirical estimation of costs and benefits incurred in decommissioning plants vis-à-vis repurposing them.
Repurposing coal plants can help overcome barriers to coal plant retirement
For power utilities, repurposing coal plants offers many advantages.
First, repurposing reduces decommissioning costs because it avoids some of the environmental remediation requirements and allows partial re-use of existing assets such as the degraded land, as well as the generators, substations and grid connections. Second, it reduces the cost of commissioning greenfield renewable capacity at the same site. Third, for coal plants located in urban and semi-urban areas, repurposing manifests in multiple end uses leading to economic diversification and industrial rejuvenation, benefiting local economies and the workforce. Fourth, it could provide a lucrative exit strategy for stranded and stressed coal plants. And fifth, repurposing coal plant equipment (e.g. the turbo-generator) allows for retaining a part of the reactive power service for voltage control originally provided by the coal plant, a valuable service when rapidly adding renewable energy.
Repurposing reduces decommissioning costs
Developed countries with significant coal capacities such as Australia, Canada, Germany, United Kingdom and the United States are taking different approaches to wean away from coal. One such approach includes retiring (i.e. decommissioning)[1] and repurposing coal plants for various productive end uses, including solar plants (e.g. in Nanticoke, Canada), wind farms (e.g. in Brayton point, U.S.), data centers (e.g. in Widows creek, U.S.), and energy storage (e.g. in Liddell, Australia).
Developing countries such as South Africa, Chile and India may gain much from the experience of their developed counterparts. Coal has played a major role in meeting the energy needs of these countries to date. However, each of these nations are now witnessing rapidly falling tariffs for renewable energy leading to accelerated penetration of renewable energy based generation into their grids, while the energy cost of coal-based generation has remained high in comparison, making its’ dispatch economically less feasible. As these countries look forward to altering their carbon footprints, repurposing considerably addresses the potential resistance to the decommissioning of coal plants, and the benefits of early coal plant retirement could create a source of funds for new renewable energy projects.
The economic case for coal plant repurposing
In order to serve as a blueprint, we examined the value proposition of repurposing using a representative 1 gigawatt (GW) Indian coal plant as a case study. Compared to similar analyses in developed countries, we believe our analysis can be useful to other developing countries with significant coal capacities. For example, in comparison to the U.S., decommissioning cost estimates for Indian plants are rather low; while the mean decommissioning costs in the U.S. are US$117m/GW, in India they are nearly half that at around US$58m/GW.
Compared to the U.S., decommissioning cost estimates for Indian plants are rather low
We calculated the present value of underlying costs, benefits, and net benefits (i.e. benefits minus costs) of repurposing coal plants for appropriate combinations of three potentially popular repurposing options – solar power, solar and battery storage, and solar and battery storage with a synchronous condenser. While the energy and flexibility value of solar energy and battery storage is well known, synchronous condensers – essentially repurposed turbo-generators from coal plants, can play a key role in providing much needed reactive power even post coal plant retirement.
We also considered both the plant specific (or direct) as well as system/society specific (or indirect) aspects of both costs and benefits. Representative examples of direct costs include jobs and environmental remediation; indirect costs include system balancing; direct benefits include salvage value and land utilization; and indirect benefits include peaking power and carbon.[2]
Our findings are as follows:
- The net benefits of repurposing coal plants are positive. The direct, indirect and total benefits of repurposing outweighed the corresponding costs of decommissioning. For instance, while the direct, indirect and total decommissioning costs were US$58.1m, US$45.8m and US$103.9m respectively; the corresponding repurposing benefits were up to US$122.8m, US$468.0m and US$590.8m. Among direct benefits, scrap value was the major contributor, and by itself covered the total direct decommissioning costs, whereas among indirect benefits, carbon benefits were the major contributor.
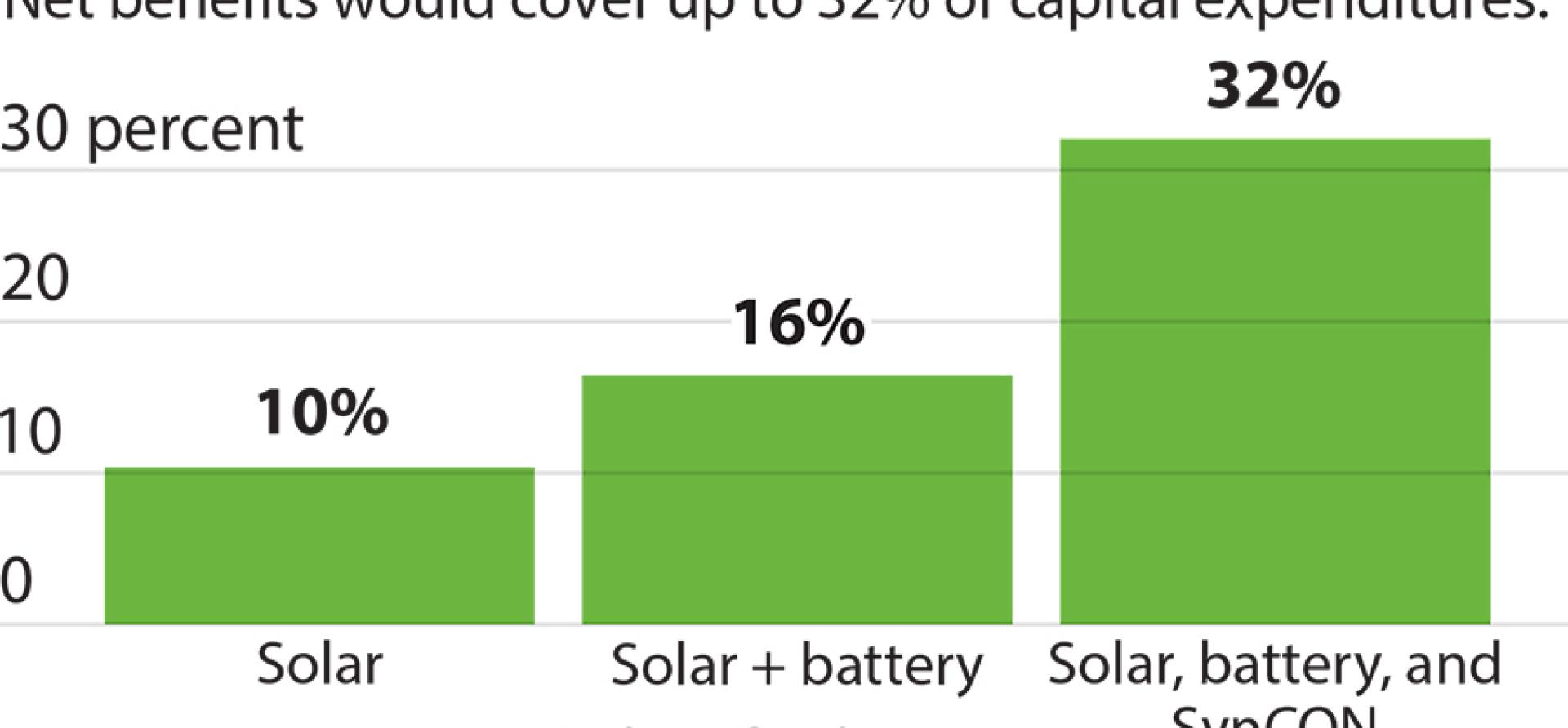
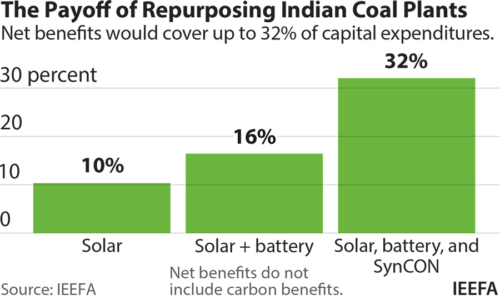
- The net benefits of repurposing covered a significant fraction of the capital expenditure in pursuing repurposing options, thus potentially improving the economics of these projects. For example, even after excluding indirect social benefits, the net benefits of repurposing covered 10.3% of solar capital expenditure; 16.4% of solar and battery storage capital expenditure; and 32.1% of solar, battery storage and synchronous condenser capital expenditure.
- Repurposing for solar and battery storage will offer higher net benefits as a percentage of combined capital expenditure into the future, given the continued rapid fall in battery prices. For instance, the net benefits of repurposing via solar and battery storage may increase from 16.4% of corresponding capital expenditure at present to 26.8% by 2029-30. Furthermore, as ancillary markets develop around the world, repurposing via a synchronous condenser would provide a major revenue stream.
Our results highlight the potential economic benefits of approaching end-of-life coal plant repurposing for utilities, the power system and society at large, including enabling the much-needed energy transition from coal to renewable energy in developing countries.
[1] Retirement means a plant stops producing electricity but its assets such as buildings, turbines etc. remain in place. Decommissioning follows retirement and entails processes relating to remediation, dismantlement, etc.
[2] For a comprehensive list of costs and benefits, see: Shrimali G, Jindal A. Cost-benefit analysis of coal-plant repurposing in developing countries. 2020.
IEEFA guest contributor Gireesh Shrimali is a Precourt Scholar at the Sustainable Finance Initiative at Stanford University and a visiting scholar at the Energy Technologies Division at Lawrence Berkeley National Lab and the Center for Climate Finance and Investment at Imperial College. Guest co-author Abhinav Jindal is a PhD Scholar in Economics at Indian Institute of Management, Indore and is working as Senior Manager (Commercial), NTPC Ltd.
Related articles:
Out-to-pasture coal plants are being repurposed into new economic endeavors
Solar is the new ruler of the Indian electricity market
‘Post-coal reclamation economy’ seen after closure of Navajo Generating Station and Kayenta Mine