Flexible exports the smart move for solar
Lack of regulation costs households millions a year in lost income
Key Takeaways:
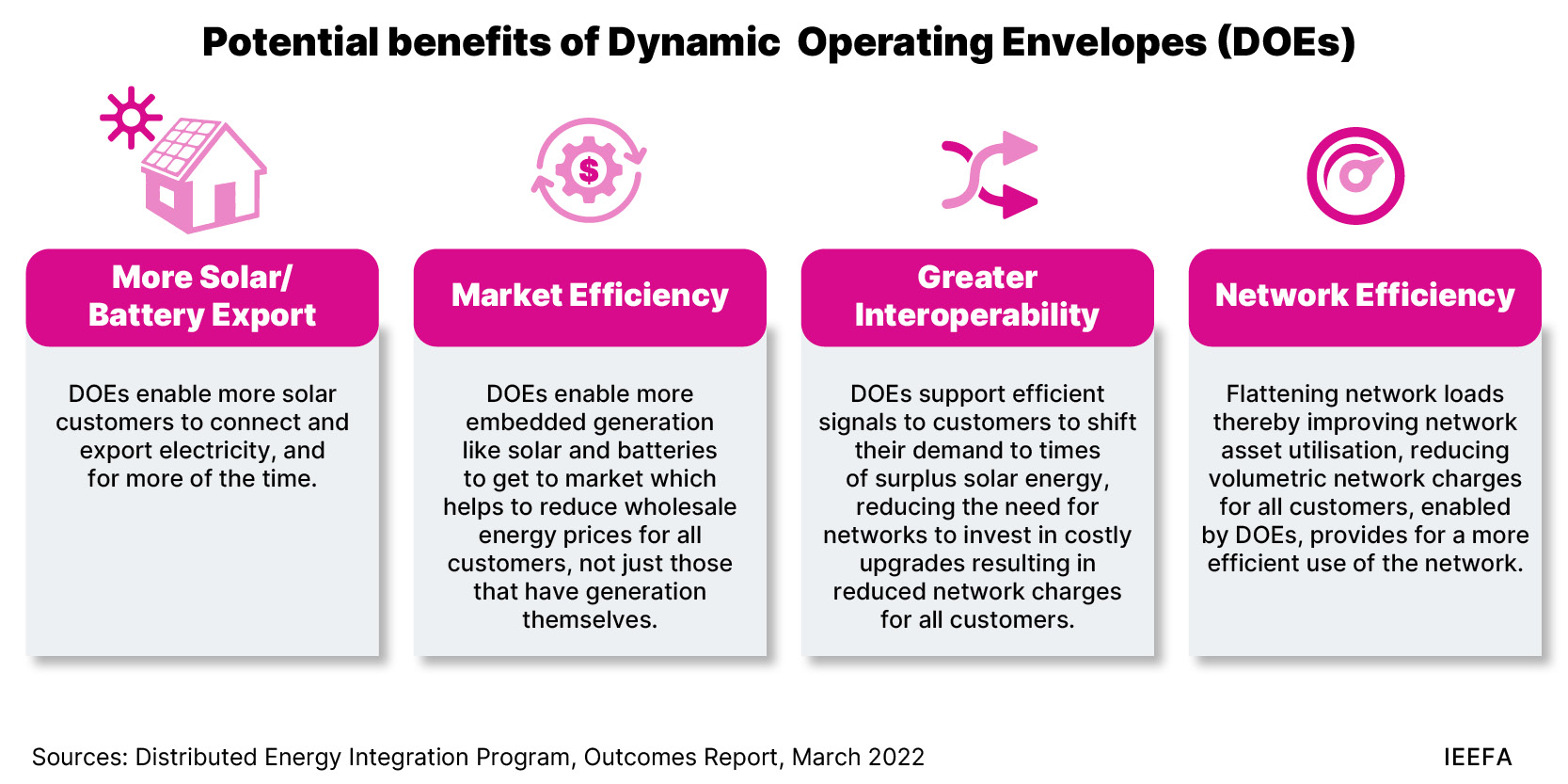
Flexible exports – enabled by smart software operated by distribution networks – could nearly double household solar exports from new systems, and reduce electricity costs for all energy consumers.
Flexible exports have been fully implemented in South Australia, but are not being rolled out consistently or quickly across the country, causing additional costs for inverter and gateway manufacturers, and unnecessarily increasing the cost to solar consumers.
We estimate that the delays to implementing flexible exports cost households installing new solar systems and those with existing 8-15kW solar systems a combined A$35 million in 2023. This cost will accumulate to A$211 million over the next three years, and will grow further if the implementation of flexible exports is delayed beyond 2026.
A rapid rule change is needed to ensure consumers benefit from fast, consistent implementation of flexible exports across the National Electricity Market (NEM).
18 December 2024 (IEEFA Australia): Rooftop solar owners are missing out on millions of dollars in income as a result of the sluggish, patchwork rollout of flexible exports, according to the Institute of Energy Economic and Financial Analysis (IEEFA).
This is due in large part to the outdated 5 kilowatt (kW) export limit imposed on rooftop solar systems in the 2000s. Today, the average rooftop solar system installed is double that capacity, but export limits have remained static, says Dr Gabrielle Kuiper, IEEFA guest contributor.
South Australia became the first state to offer flexible exports of solar energy as standard. SA Power Networks developed software to forecast the network’s hosting capacity 24 hours in advance, on a five-minute basis, to safely and dynamically manage solar inflows of up to 10kW per inverter.
In her briefing note, How rapid implementation of flexible exports could maximise rooftop solar, Dr Kuiper highlights how the inconsistent rollout of flexible exports is costing consumers across Australia millions a year in lost income – A$35 million in 2023 alone. That figure is expected to balloon to A$211 million over the next three years as more solar systems are installed.
“All electricity system users benefit from the additional exports since the increased energy supply can reduce electricity prices for everyone,” Dr Kuiper says.
“SA Power Networks modelling shows flexible exports will likely be set below the doubled 10kW limit only 2% of the time or approximately 50 daylight hours per year.
“This is extraordinary, especially given about half of households already have rooftop solar installed in the SA Power Networks area, and at times rooftop solar supplies more than the state’s total electricity demand.”
This extra energy can be used to partially displace large generators in wholesale supply, support local networks, and to stabilise the grid, unlocking an estimated A$5.08 billion in net benefits for all consumers to 2042, according to a Deloitte cost-benefit analysis.
However, equipment manufacturers and installers, and ultimately consumers, are disadvantaged by the inconsistent, inefficient, slow or non-existent rollout of flexible exports due to the lack of uniform national regulations.
“The implementation across six jurisdictions by 11 different distribution network service providers (DNSPs) is being planned or delivered using a variety of standards and devices,” Dr Kuiper says.
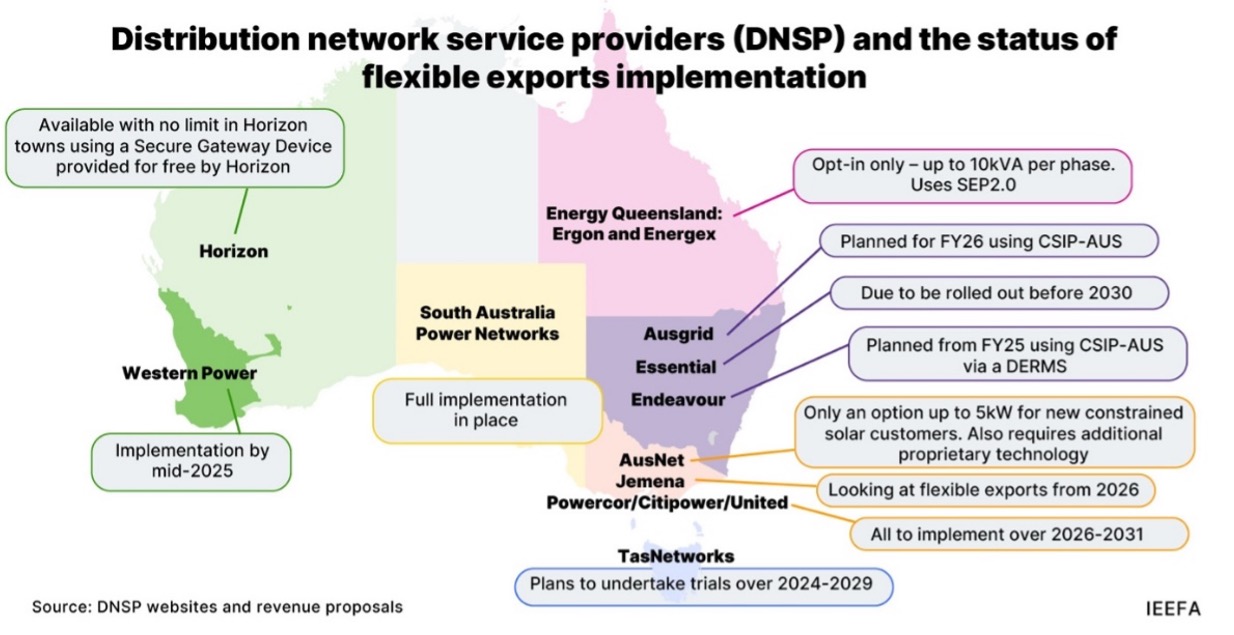
“Unless there is a nationally consistent approach to communication and integration, meeting all requirements for all DNSPs will be a huge undertaking by industry.
“What does this mean for the consumer? It will push up the cost of doing business in Australia for manufacturers, which ultimately will make Australia less appealing with higher product and installation costs than any other global region.”
Basic requirements could be put in place to minimise the costs of compliance by inverter manufacturers with flexible exports across different DNSP areas. These include:
- Communication protocol from the DNSP to the inverter.
- Testing and certifying equipment.
- Data communication standards.
- Flexible exports communication.
- Visibility of DOEs to VPP operators/aggregators.
- Behind-the-meter (BTM) access.
“It is in the interests of consumers that these be put in place as soon as possible, given that approximately 300,000 household solar systems are being installed annually and the financial benefits calculated above,” Dr Kuiper says.
“The Commonwealth Minister should lodge a rule change to look at options to manage minimum system load (including the ‘emergency backstop’ mechanism) and the fast implementation of flexible exports. Both issues affect the management of customers’ rooftop solar systems, and should be addressed jointly to ensure the best technical and social outcome.”
Read the analysis: How rapid implementation of flexible exports could maximise rooftop solar
Media contact: Amy Leiper, ph 0414 643 446, [email protected]
About IEEFA: The Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) examines issues related to energy markets, trends, and policies. The Institute’s mission is to accelerate the transition to a diverse, sustainable and profitable energy economy. (ieefa.org)