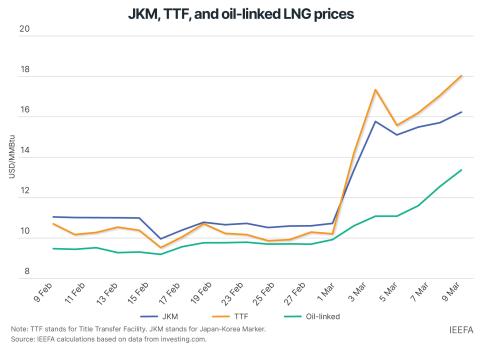
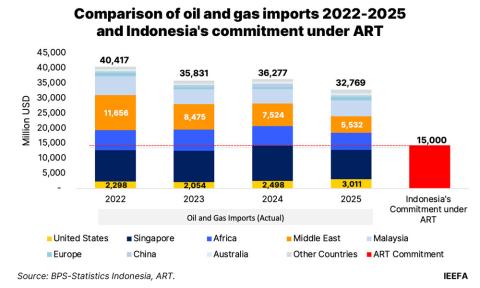
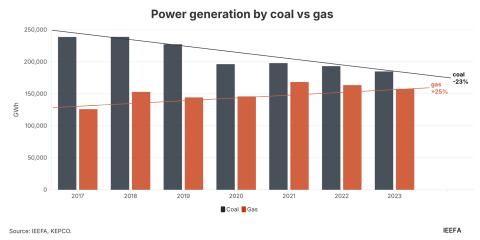
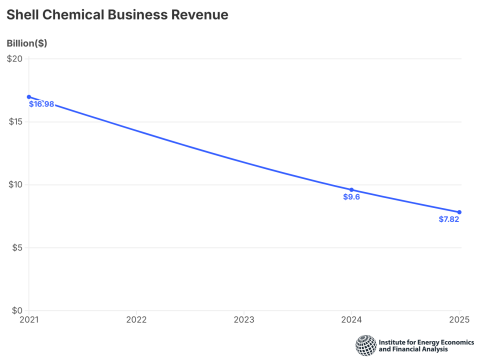
Global crises must not push clean energy down the agenda

Key Findings
There is a danger that as governments turn inward to deal with food and energy crises, climate goals slip down agendas.
COP27 presents an opportunity for countries to enhance their ambition to deploy solutions that can address global warming and speed up the transition away from expensive fossil fuels.
India can take the lead in representing the demand for access to the latest technology and the need for more finance for climate adaptation and mitigation – not only for itself but also for other developing economies.
It’s that time of year when countries undergo a ‘health check’ on their progress towards climate goals, followed by discussion on how their scorecards can be improved.
As leaders convene in Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt for COP27, the annual U.N. climate change conference, it is clear that countries are not doing enough to meet their nationally determined contributions (NDCs) submitted under the Paris Agreement.
Countries are not doing enough to meet their nationally determined contributions (NDCs).
Climate activist Greta Thunberg is among the notable absences this year. Although the new UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak made a swift U-turn and is now attending the summit after facing criticism from climate campaigners and opposition parties.
Risk of backtracking on climate ambition
There is a danger that as governments turn inwards to deal with food and energy crises, climate change goals slip down agendas. However, COP27 presents an opportunity for countries to enhance their ambition and deploy solutions that can address global warming and speed up the transition away from expensive fossil fuels.
Just when the world was coming to terms with the impact of Covid-19, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine exacerbated the issue of energy security and caused commodity and fuel prices to surge, leading to high inflation and high interest rates, currency devaluation etc. Many countries, including India, are now facing a double whammy of high inflation and high interest rates which is impacting economic growth and consumer well-being.
Further, in 2022, massive flooding hit Pakistan and Puerto Rico, while heatwaves in South Asia and Europe drove up energy demand. Extreme weather conditions have caused loss of life and property.
This year, European nations backtracked on climate ambition after Russia cut gas supplies. Germany, Italy, Austria and the Netherlands are among countries resorting to reviving coal-fired power generation. Such actions dilute the position of developed countries as climate leaders and their ability to call upon developing countries to enhance their climate goals.
India can lead the push for climate finance
India submitted its revised NDC in August 2022. It has committed to reducing the emissions intensity of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by 45% from 2005 levels by 2030, strengthening its target from 33-35%, and to have 50% of installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based power sources by 2030, from 40% earlier. These commitments are unlikely to be enhanced in Egypt.
Countries in the Global South, which are bearing the brunt of climate impacts linked to emissions from the Global North's economic development, are calling for climate justice and equity. India can take the lead in representing the demand for access to the latest technology and the need for more finance for climate adaptation and mitigation – not only for itself but also for other developing economies.
The target of US$100 billion per year in climate finance by 2020 from the developed world, which has yet to be achieved, is minuscule compared to the quantum of capital required by developing economies. The world needs to channel much more money from public sources as well as private capital, which is currently where a large majority of financial wealth is held.
The world needs to channel much more finance for climate adaptation and mitigation, from public sources and private capital.
Debt in the form of both conventional and sustainable capital comprising of green bonds and loans, sustainability linked bonds and loans etc. needs to flow in. On the equity side, long-term patient capital, such as pension funds, insurers and sovereign wealth funds can play a big role.
Multilateral development banks (MDBs) are another sizeable and often critical climate finance source, especially for funding technologies in sectors where private capital would not invest, either because the technologies are at a nascent stage of growth or offer low returns.
Further, emerging countries with limited financial resources are going to demand finance for “loss and damage”. They will ask for a separate fund to help rebuild and cope with losses due to increased incidences of natural calamities.
However, there are questions around whether developed countries – which have broken their promise of US$100 billion annually by 2020 and are further impacted this year by high prices due to the Ukraine war – will commit to any additional funding. Or would this be a subset of building climate-resilient infrastructure, which is based on an earlier commitment?
2022 has been a difficult year. In fact, Collins Dictionary's word of the year is ‘permacrisis’, meaning an extended period of instability and insecurity, sums it up well.
The world cannot afford to lose a year in the climate race. Despite these short-term hiccups, the long-term pathway must be clean and green.
As U.N. Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said, instead of countries “hitting the brakes” on decarbonising the global economy in the wake of Russia’s invasion, “now is the time to put the pedal to the metal towards a renewable energy future.”
Countries urgently need to accelerate towards cheaper renewable energy. This will require investing in an entire ecosystem around renewable energy sources, with better technologies for energy storage and modules that will improve utilisation factors for renewable energy, and developing nascent technologies like offshore wind and green hydrogen.
This article was first published by the Economic Times