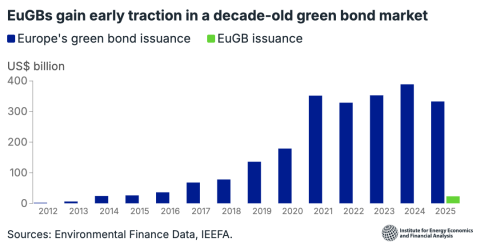
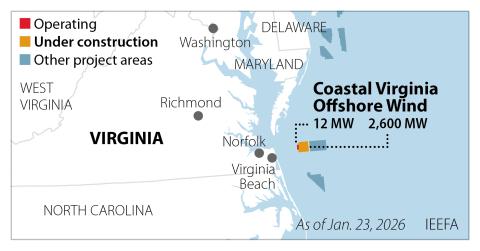
Key Findings
The European Union has reduced the volume of natural gas from Russian pipelines, but its imports of liquefied natural gas have increased sharply.
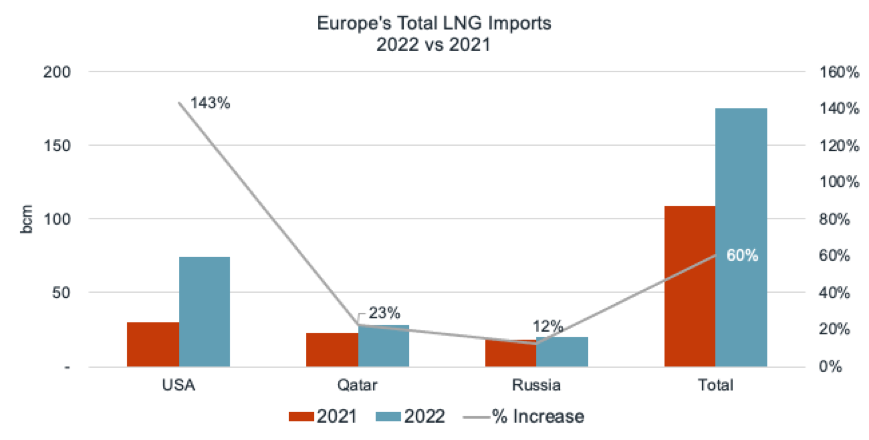
The majority of LNG imports came from the United States (143 percent increase from 2021) and Qatar (23 percent). Imports of Russian LNG rose 12 percent.
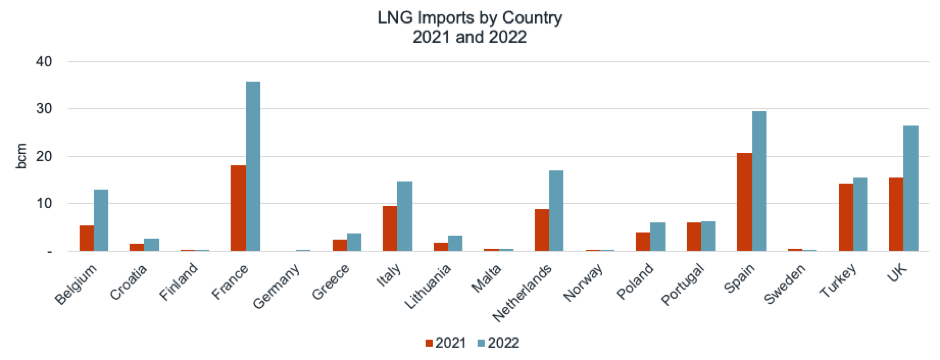
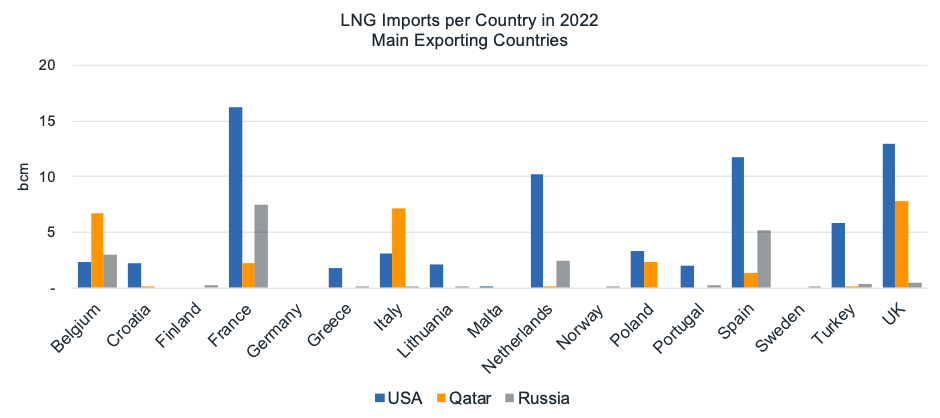
France was the top importer of LNG from both the United States and Russia, while the UK was the top importer of LNG from Qatar.
Gas-fired generation increased in 2022, partly to compensate for a series of factors that included a lack of rainfall that reduced hydroelectric production in EU countries; record nuclear outages in France; and the Iberian exception.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine greatly affected the traded volumes of imported piped gas and liquefied natural gas (LNG) in Europe. Since the start of the conflict, piped gas imports from Russia to Europe have been significantly reduced; LNG imports have sharply increased.
In 2021, the EU imported about 155 billion cubic meters (bcm) of natural gas from Russia, while Turkey and the United Kingdom imported around 16 bcm and 3 bcm, respectively.
Europe's LNG imports increased 60 percent in 2022 from the previous year. The majority came from the United States, Qatar and Russia. LNG imports from the United States increased by 143%, and imports from Qatar increased by 23%.
Despite the adoption of the Versailles Declaration in March 2022, when leaders of the 27 EU member states pledged to phase out the EU’s dependence on Russian fossil fuels as soon as possible, imports of Russian LNG increased by 12% in 2022 compared to 2021.
Source: IHS Markit, IEEFA
The increase occurred against the backdrop of a reduction in pipeline gas imports, which magnified the energy price crisis and led to an increase in LNG imports. France, Spain, the UK, the Netherlands, Italy, Turkey and Belgium were the top LNG importers in 2022.
Gas-to-power generation increased across the continent in 2022, partly to compensate for a series of factors that included a lack of rainfall that reduced hydroelectric production in EU countries; record nuclear outages in France; and the Iberian exception, a price cap that applies exclusively to gas for power generation in Spain and Portugal, among others.
Source: IHS Markit, IEEFA
In 2022, France was the top importer of LNG from both the United States and Russia, while the UK was the top importer of LNG from Qatar.
Source: IHS Markit, IEEFA
Over the past year, the EU has promoted LNG as a solution to enhancing the diversity of gas supply and improving energy security, and has encouraged widespread access to the LNG market across all its member states.
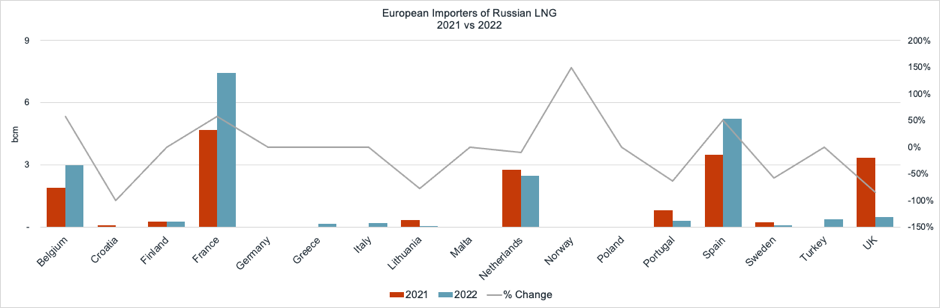
While Russian piped gas supplies to the EU decreased in 2022, some countries have continued importing Russian LNG, working against a commonly agreed goal of ensuring energy security and cutting dependence from Russian sources.
The top importers of Russian LNG in 2022 were France, Spain, Belgium and the Netherlands. France, Spain and Belgium significantly increased imports of Russian LNG, by 55% in total.
By contrast, Croatia, Lithuania, Portugal, Sweden and the UK sharply reduced their imports of Russian LNG in 2022. The UK’s Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office announced Jan. 1 that the country would halt imports of Russian LNG.
Source: IHS Markit, IEEFA
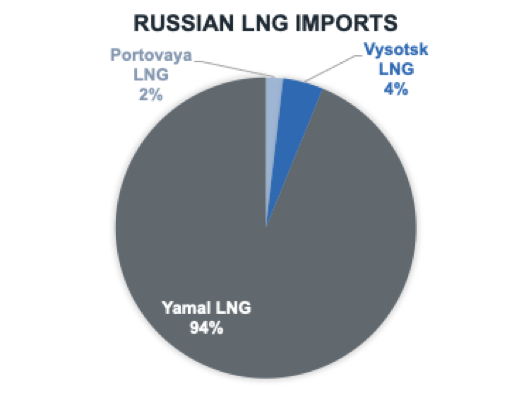
Virtually all 94% of Russian LNG imports came from the Yamal LNG Terminal, an integrated project encompassing natural gas production, liquefaction and shipping. The terminal, located on the Yamal Peninsula, utilises the resources of the South Tambey Field.
Source: IHS Markit, IEEFA
Yamal’s LNG plant has an output capacity of around 16.5 million tons per year and is operated by JSC Yamal LNG, a joint-venture of Novatek (50.1%), TotalEnergies (20%), the China National Petroleum Company (20%) and Silk Road Fund (9.9%).
The main long-term LNG buyers from the Yamal facility are China's CNPC, Gazprom Marketing & Trading, Naturgy (a Spanish multinational natural gas and electrical energy utilities company), Novatek and TotalEnergies.