India saw record investment in renewables last financial year – so what next for green power in the country?

Key Findings
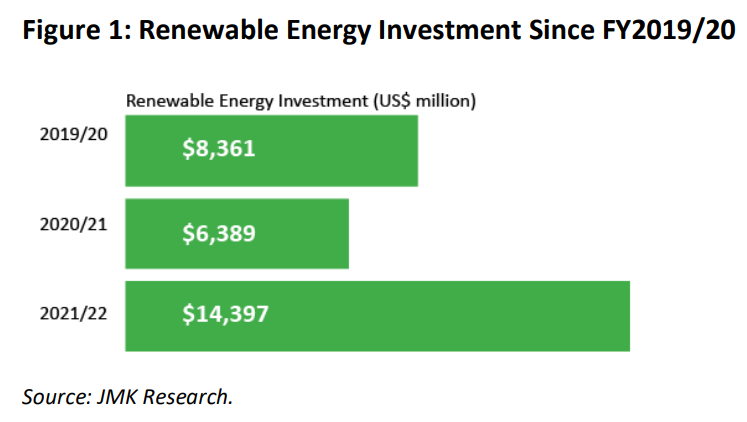
Investment in renewable energy hit a record level in India during the last financial year.
A total of US$14.5 billion was invested in renewable energy in India, up by 125% compared with financial year 2020-21 and 72% higher than in the pre-pandemic period of the 2019-20 financial year.
For India to reach its target of 450GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, investment in renewables will need to more than double to about US$30-US$40 billion per year.
Investment in renewable energy hit record levels in India in the 2021-22 financial year, according to a recent IEEFA report.
A total of $14.5 billion was invested in renewable energy, up by 125% compared with financial year 2020-21 and 72% higher than in the pre-pandemic period of the 2019-20 financial year.
To understand the latest on renewable energy in India, the World Economic Forum spoke to the report's author Vibhuti Garg by email. Here's what she said.
1. The report says that India has committed to reaching 175GW of renewable capacity by the end of 2022, and increased its 2030 goal to 450GW. Is the country on track to do this, given the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic?
Vibhuti Garg: In 2016, India set a target of teaching 175GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022, comprising 100GW of solar, 60GW of wind, 10GW of biomass power and 5GW of small hydropower.
But with just seven months of 2022 remaining, only around 57% of the 100GW solar target and 67% of the wind target has been met. This means India is projected to miss its 2022 solar and wind capacity targets by about 27% and 18%, respectively.
The shortfall in solar capacity is mainly from rooftop solar. Utility-scale (grid-scale) solar capacity is largely on track. Headwinds ranging from COVID-induced supply chain disruption to deeply rooted policy restrictions are holding back the growth of the rooftop solar market in India.
For wind, reverse bidding auctions led to better price discovery, but also encouraged aggressive bids. Renewable energy developers found it increasingly difficult to deliver at these lower prices. Also, the best sites for wind energy, which are located in coastal areas of Tamil Nadu and Gujarat, have already been exploited. New sites have lower capacity utilization factors, resulting in higher prices.
India's electricity demand fell during COVID, but it rose sharply as industrial activity picked up, and the recent extreme heat has pushed up demand for cooling. High electricity demand will drive the installation of more renewable energy capacity in the next few months.
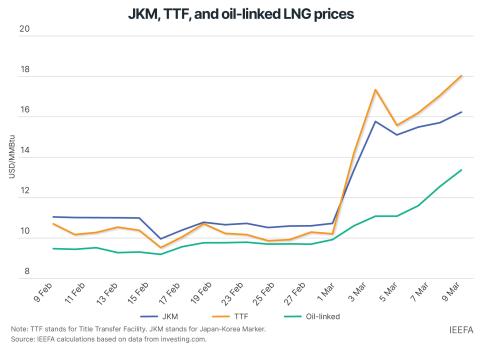
Renewable energy prices are falling, and renewables are now a cheaper source of electricity than coal-based power. The Russia-Ukraine war has driven up the prices of imported coal and gas and is adding strain to the dispatchability of high-cost power. Renewable energy combined with energy storage systems such as battery storage and pumped hydro have become a cheaper source of electricity to meet electricity demand round the clock.
2. Which areas are the key drivers of India's renewables growth right now, and do you see this trend shifting at all over the coming decade, towards other technologies?
Vibhuti Garg: Rising electricity demand, falling prices for renewable energy, India’s push to manufacture solar photovoltaic modules, government support schemes aimed at boosting Indian manufacturers’ competitiveness and attracting investment (Production Linked Incentive schemes), and the waiver of transmission charges for renewable energy are the key drivers of India's renewable energy growth right now.
The growth trend will continue, but renewables need support from the government. The issuing of big tenders for energy storage and supportive policies for green hydrogen will accelerate the roll-out of clean energy technologies to decarbonize not just the electricity sector but also other hard-to-abate sectors like fertilizer production and petroleum refining. Government policy so far has provided a boost from the supply side. The government can further support these positive developments by implementing a green hydrogen consumption obligation mechanism for fertilizer production and petroleum refining, similar to the renewable purchase obligations that require a minimum percentage of electricity to be bought from renewable energy sources. This would provide strong offtake visibility for developers and incentivize investment into production facilities.
Energy storage systems are another growth area. The government has realized that energy storage will be critical to achieving India's renewables targets and has come up with initiatives and policy support for the sector. It has waived inter-state transmission system charges for energy storage projects commissioned before June 2025. In addition to issuing standard bidding guidelines for energy storage systems in March 2022, the government is working on a National Energy Storage Policy to address major impediments facing the industry. Also, a time-based target in the upcoming policy – similar to India's targets for renewable energy – would act as a key driver for growth in energy storage.
The government is now also pushing for offshore wind. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has revived its offshore wind power development goals by unveiling a roadmap for installing 30GW by 2030. With offshore project costs falling globally, it's the right time for this move.
3. How much can India do with hydrogen, and how quickly? The government has launched a roadmap with incentives for investors.
India has a target of 5 million tonnes a year of green hydrogen capacity by 2030. While this is ambitious, some major developers have made big financial commitments to green hydrogen in India.
Recent green hydrogen announcements include:
-
At the recent World Economic Forum Annual Meeting in Davos, Indian renewable energy developer ACME signed a memorandum of understanding worth $7 billion with the state government of Karnataka to develop an integrated solar to green hydrogen to green ammonia facility that will produce 1.2 million tonnes a year of green hydrogen by 2027.
-
In June, French oil and gas giant TotalEnergies announced another partnership with Adani Group subsidiary Adani New Industries to invest $50 billion over 10 years to produce green hydrogen.
-
In April, Indian renewable energy developer ReNew Power announced a joint venture with state-run Indian Oil Corporation and engineering and construction major Larsen & Toubro for green hydrogen production.
4. The report says 'investment in renewables would need to more than double to about $30 billion-$40 billion per year for India to reach its target of 450GW by 2030'. What is being done to promote this investment at a time of rising inflation, when budgets are tight across the globe?
The Indian government has rolled out policies and reforms to facilitate the growth of the renewable energy sector and is now facilitating investment in other clean technologies, such as energy storage, green hydrogen, energy efficiency and electric mobility.
A large part of the climate finance needed by India can come from sustainable finance markets, which have grown in leaps and bounds over the last couple of years.
Until now Indian companies have struggled to attract a large part of this capital pool due to shallow and illiquid domestic capital markets (especially for debt) which restrict investment opportunities and increase illiquidity risks, a lack of transparent, consistent and comprehensive environmental social and governance (ESG) disclosures, and concerns about greenwashing.
However, India has been trying to tackle these problems through regulatory reforms such as mandatory ESG reporting. It has also been working towards regulating ESG ratings and data products and has a proposed green taxonomy.
5. How do India's renewable energy prospects and potential compare to those of other countries?
India has massive renewable energy potential that has yet to be fully exploited. It is also a large developing economy with huge energy demand growth. The country not only needs to make a seismic shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy, but also has new incremental demand that needs to be met through additional renewable energy capacity.
So India is facing a bigger challenge than many other countries in that it must set up a huge amount of renewable energy capacity for which it will need cheaper financial resources and greater access to clean energy technologies.
Also, wind and solar energy are intermittent, so India needs to build an entire ecosystem around renewable energy. This involves:
-
Investing in flexible generation sources like battery storage and pumped hydro.
-
Expansion of transmission and distribution networks.
-
Modernization and digitalization of the grid.
-
Domestic manufacturing of inputs like solar modules, solar cells, wafers and electrolyzers.
-
Promoting electric vehicles.
-
Promoting more decentralized renewable energy like rooftop solar.
This article first appeared on weforum.org