KEXIM delays investment in Santos’s Barossa gas project despite the company’s carbon capture aspirations, citing concerns
8 April 2022 (IEEFA Australia): Santos’s recently released 2022 Climate Change Report buries its recent emission increases and relies heavily on carbon capture technologies and blue hydrogen to achieve future emission reductions according to a new report by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), a fact perhaps affecting yesterday’s announcement by the Import-Export Bank of South Korea’s (KEXIM) board to delay a $330 million credit facility for the Barossa gas project in Australia, citing environmental and legal factors.
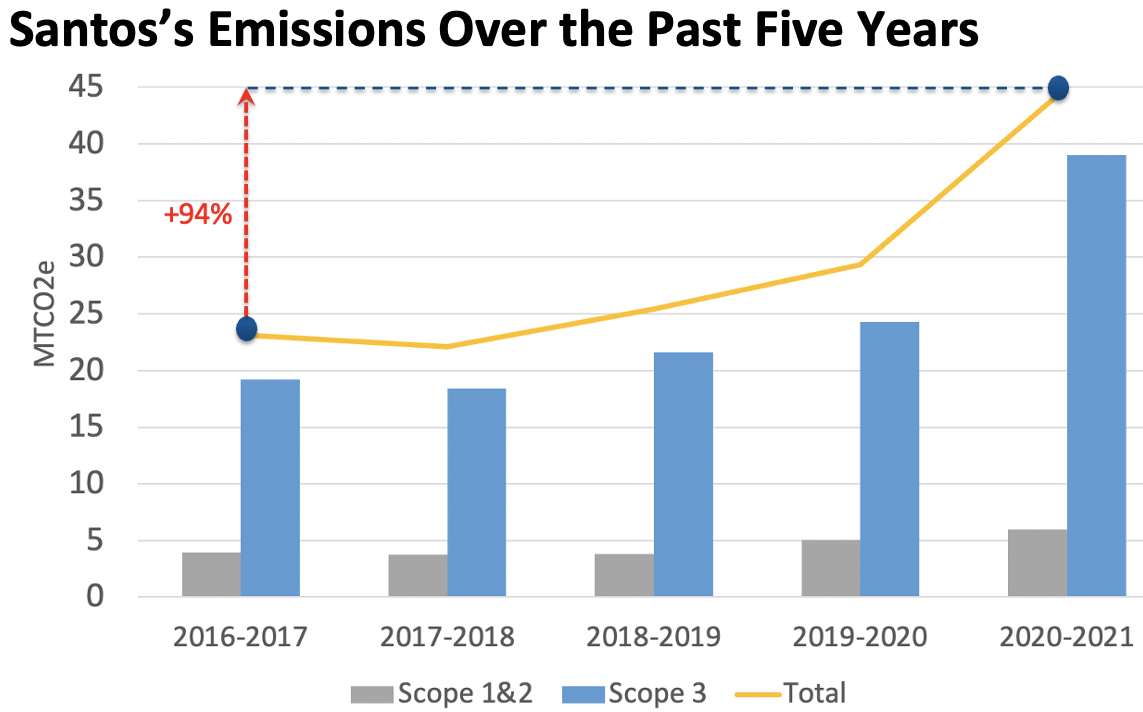
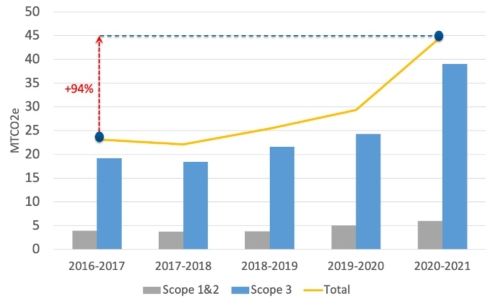
Santos’s total emissions grew by 94% over the past five years
Despite targeting net-zero, Santos’s total emissions grew by 53% over the year to June 2021 and by 94% over the past five years, according to its 2022 Climate Change Report.
“This may be raising significant concerns for investors considering its billion dollar oil and gas expansion plans for 2022 alone,” says report author IEEFA LNG/gas analyst Bruce Robertson.
“Overall, Santos’s considerable capital expenditure budget in 2022 – between US$1.15 billion and US$1.3 billion, will mostly be spent on oil and gas expansion projects including a new project at Barossa.
“New oil and gas projects are not consistent with any net-zero emissions by 2050 scenario. Producing more emissions is not emissions reduction.
“Investors in Barossa, like KEXIM, appear to be judging Santos and the companies involved by their actions, not their aspirations.”
Robertson says even with carbon capture and storage, the new Barossa gas project will increase emissions, not decrease them, and so is entirely inconsistent with Santos’s 2022 Climate Change Report’s stated aim of reducing emissions.
Investors in Barossa appear to be judging Santos and the companies involved by their actions
“Most of the Barossa project’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions will be from combustion, which cannot be captured. CO2 capture processes post-combustion are not currently economically feasible onshore, let alone offshore, anywhere in the world.
“Even with CCS, Santos’s proposed high emitting Barossa project remains an emissions factory with an LNG by-product – more waste than product.
“Reliance on carbon capture, a technology with high failure rates despite its 50 year history, is a fig leaf to disguise rising emissions in the oil and gas industry.”
Co-author IEEFA energy analyst Milad Mousavian says carbon capture has proven to be technically difficult to implement, saving only fractions of the emissions initially promised.
“ExxonMobil’s Shute Creek CCUS plant and Chevron’s Gorgon CCS plant are two of the biggest carbon capture projects in the world and both have seriously underperformed their targets.
“ExxonMobil sold the CO2 it captured to oil and gas companies to get more oil out of the ground thereby increasing oil and gas production, not reducing emissions, and Gorgon underperformed its targets for the first five years by more than 50% and is now facing payments of up to hundreds of millions of dollars in carbon credits to make up for the shortfall.”
Blue hydrogen is not emissions friendly
IEEFA’s report notes Santos is also looking to blue hydrogen – hydrogen produced with gas and carbon capture and storage – to reduce emissions.
“Blue hydrogen is not emissions friendly, producing more emissions than just burning the gas, according to some recent scientific studies,” says Mousavian.
“At current gas prices it not competitive with hydrogen produced with renewable electricity, labelled green hydrogen.
“It’s difficult to see how Santos will materially reduce emissions along the customers’ value chain. Investors should be wary.”
Robertson says Santos’s stated rapidly increasing emissions is sobering, particularly when you consider the systemic under-reporting of emissions globally by the oil and gas industry.
“While the oil and gas industry, as a whole, releases 42% of global emissions, the International Energy Agency has stated that methane emissions from the energy sector are 70% higher than official figures.
“Santos’s real emissions are most probably understated by a considerable margin.”
Santos’s Emissions Over the Past Five Years
IEEFA’s report notes there is escalating pressure from stakeholders, regulators and civil societies on oil and gas companies to take their liability for Scope 3 emissions into account. Consequently, some big companies such as Eni, Total and BP have adopted “absolute measures” to reduce their Scope 3 emissions.
Santos has a target of reducing Scope 3 emissions by 1.5 million tonnes per year, representing only about 4% of its Scope 3 emissions in 2020-2021. Its planned Scope 1 and 2 emission 2030 targets would reduce total emissions by only about 4% of its 2020-2021 total emissions.
“KEXIM’s decision highlights how oil and gas companies are on notice,” says Robertson.
“Investor funding of high emitting projects like Barossa is not assured anymore.”
Read the report: Santos 2022 Climate Change Report – A Reality Check. The Scorecard Shows Emissions Climbed Steeply, and Understates the True Position
Media contact: Kate Finlayson ([email protected]) +61 418 254 237
Author contact: Bruce Robertson ([email protected]) and Milad Mousavian ([email protected])
About IEEFA: The Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) examines issues related to energy markets, trends, and policies. The Institute’s mission is to accelerate the transition to a diverse, sustainable and profitable energy economy. (ieefa.org)