IEEFA: What India can learn from Australia’s distributed energy transformation
31 March 2021 (IEEFA India): Policy makers and regulators must build the framework required for combining rooftop solar with battery storage and electric vehicles to meet Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision for a sustainable, energy-secure future, according to a new report from the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA).
Prime Minister Modi wants India to be a 100% EV nation by 2030
In addition to the ambitious renewable energy target of reaching 450 gigawatts (GW) by 2030 and media reports suggesting consideration of a mid-century net-zero emissions target, Prime Minister Modi wants India to be a 100% electric vehicle (EV) nation by 2030.
“Combining rooftop solar plus storage in the form of batteries and EVs, or mobile batteries, are in India’s near-future,” says co-author Vibhuti Garg, IEEFA Energy Economist, Lead India.
“Policy initiatives by central and state governments are already boosting the adoption of EVs, and although slow, rooftop solar and battery uptake is increasing.
“What’s missing however is the opportunity to integrate distributed energy and therefore maximise the benefit of combining rooftop solar with small-scale storage, smart demand-responsive appliances and EVs.”
IEEFA’s report suggests policy makers will need to make the technical integration of these distributed energy resources (DER) a priority.
“There are several lessons India could learn from Australia when it comes to technical integration of solar, storage and EVs,” says co-author Dr Gabrielle Kuiper, a DER specialist and IEEFA guest contributor.
“Putting in place a technical standards framework, appropriate quality controls and consumer protections for distributed energy products and installations, and appointing a respected agency to ensure compliance, will be critical in shoring up consumer and investor confidence.”
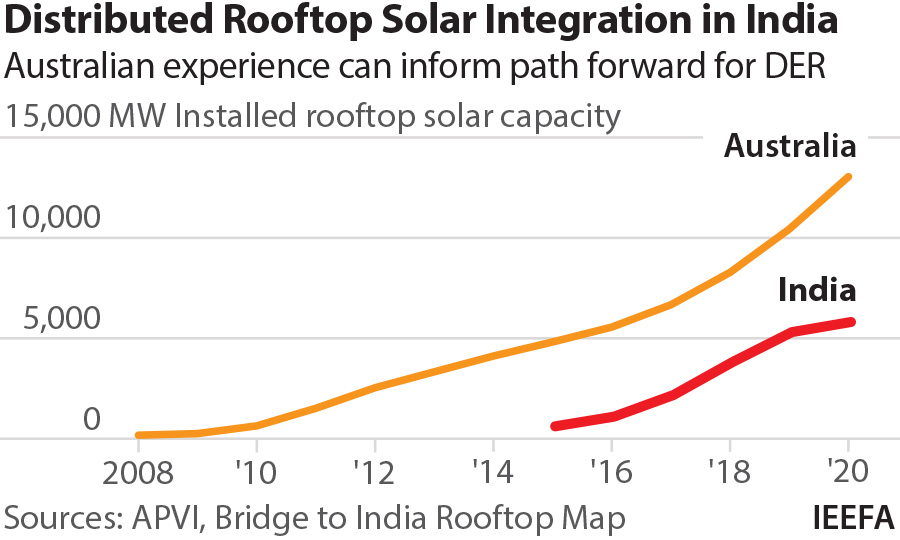
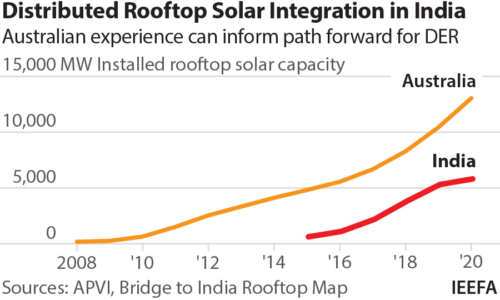
Australia is at the forefront of the distributed energy revolution with the world’s highest rooftop solar capacity per person (786 watts) and a record rate of new installations (3 gigawatts in 2020, a 39% increase on a year-on-year basis). Roughly one in four Australian households – about 2.7 million homes – have rooftop solar systems, and increasingly battery storage.
India, meanwhile, is on the cusp of its own distributed energy transition as the government steps up support for uptake of rooftop solar and solar irrigation pumps, and targets 15% of vehicle sales to be electric by 2023.
Combining rooftop solar with storage and EVs is key
“Combining rooftop solar with storage and EVs is key,” says Dr Kuiper. “It is more cost effective for private and public consumers to have distributed charging co-located with power generation and to directly charge EVs using behind-the-meter solar.”
Managed charging and discharging of EVs and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology – which enables power to be drawn from or supplied to the grid when most needed – could be a game-changer for India.
An additional time-of-day price signal to incentivise supply in peak demand periods will provide much-needed flexibility in the Indian grid as the proportion of variable renewable energy grows.
At 5.9GW, rooftop solar comprises only one-sixth of India’s total solar capacity and is a long way off the government’s target of 40GW of installed rooftop solar capacity by 2022.
Garg says distribution companies (discoms) could play a greater role in facilitating a system where distributed energy resources like rooftop solar, battery storage and EVs are central, planned for and taken advantage of, driving deflation and sustainable energy for all.
“Discoms are watching their high-paying commercial and industrial consumers install private supplies of rooftop solar plus storage which is undermining discoms’ revenues due to their excessive reliance on unsustainable cross-subsidies.
Discoms could proactively offer rooftop solar plus storage packages
“Instead, discoms could proactively offer rooftop solar plus storage packages and change the customer landscape.”
Garg says the pace of distributed energy uptake and integration will need to accelerate for India to drive decarbonisation, improve energy self-reliance and achieve its ambitious renewable energy targets.
“This is likely to come to the fore of discussions if reports the government is considering a mid-century net-zero emissions target are confirmed.”
Read the report: Lessons from Australia for India on Integrating Distributed Energy Resources (DER)
Media contact: Rosamond Hutt ([email protected]) +61 406 676 318
Author contacts: Dr Gabrielle Kuiper ([email protected]); Vibhuti Garg ([email protected])
The authors are available for interviews or background briefings.
About IEEFA: The Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) examines issues related to energy markets, trends, and policies. The Institute’s mission is to accelerate the transition to a diverse, sustainable and profitable energy economy. (www.ieefa.org)