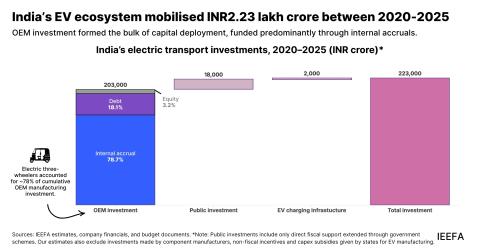
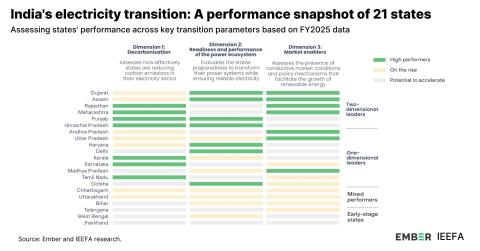
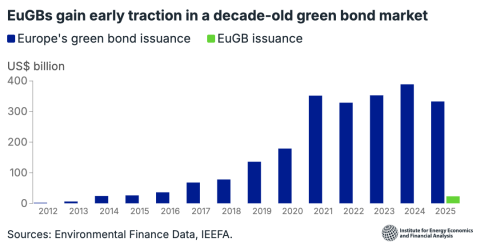
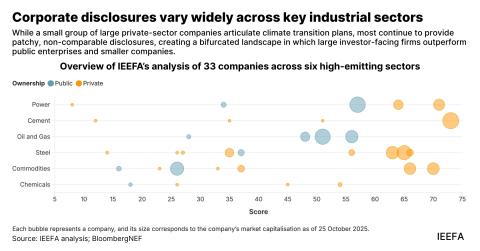
IEEFA India: Proposed Khurja coal power plant overpriced, uncompetitive and another threat to Delhi’s air quality
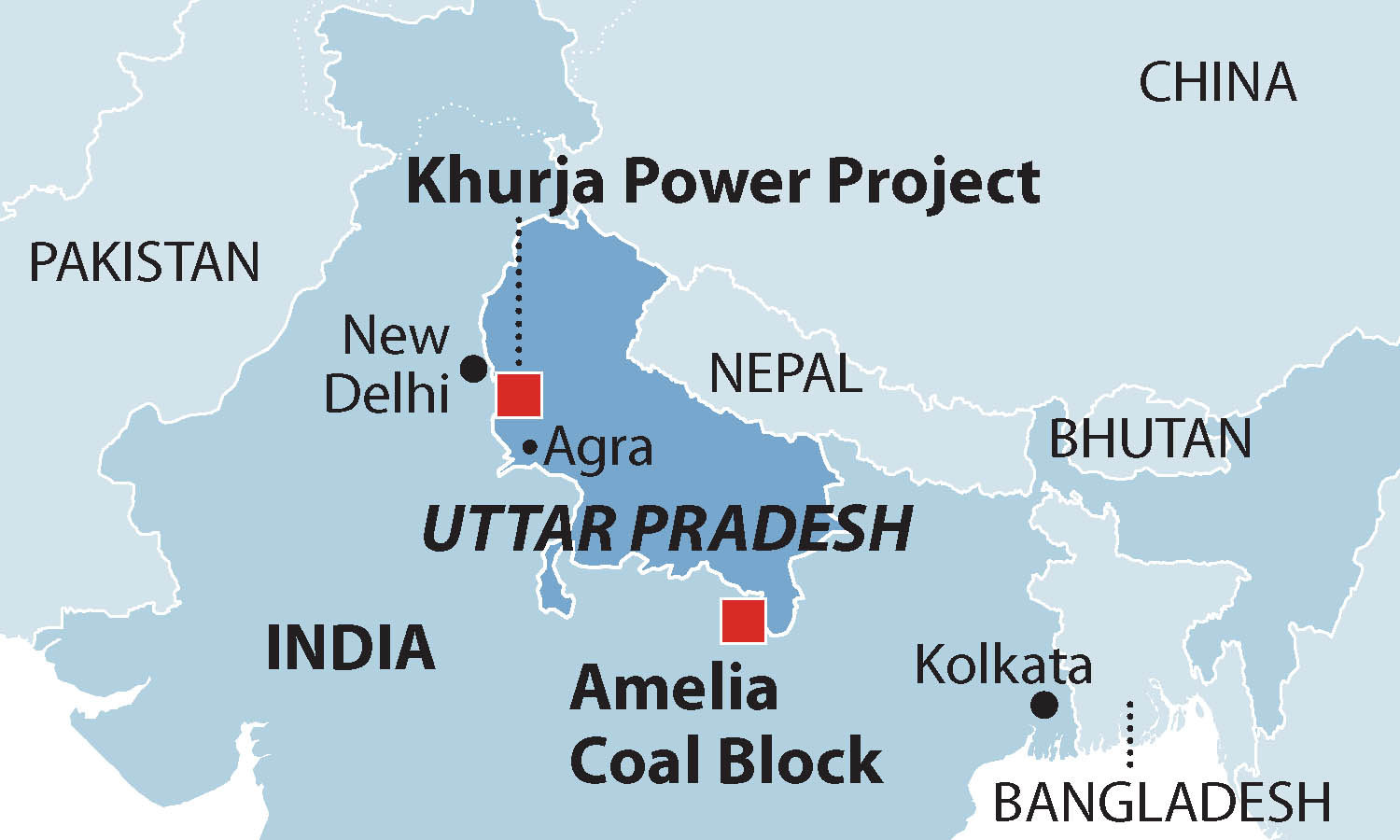
Oct. 23, 2018, NEW DELHI (IEEFA) – A report published today by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) evaluating Tehri Hydro Development Corporation (THDC)’s proposed Khurja coal power plant in India finds the plant would push up the cost of electricity and increase air pollution at a time when the country’s renewable energy options are cheaper, accessible and more sustainable.
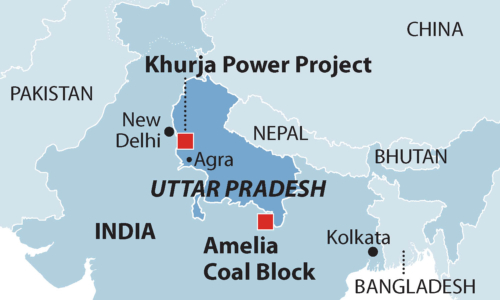 Released at an energy roundtable in Delhi this morning, the report The Khurja Thermal Power Project: A Recipe for an Indian Stranded Asset recommends the proposed Khurja coal power plant be cancelled, due to:
Released at an energy roundtable in Delhi this morning, the report The Khurja Thermal Power Project: A Recipe for an Indian Stranded Asset recommends the proposed Khurja coal power plant be cancelled, due to:
- site location and current emergency air pollution levels in Delhi,
- the real threat of government finance being wasted on another expensive stranded asset,
- the costly interstate import price of coal,
- the likely lower than modelled utilisation rate of the Khurja power plant,
- the lower than expected electricity demand growth,
- increasingly cheaper, deflationary, domestic renewable energy options, and
- India’s ambitious sustainable energy goals.
Tim Buckley, IEEFA Director of Energy Finance Studies, said electricity users, the state and central government, and the project’s lenders should not be burdened with yet another expensive stranded asset at a time when local residents need cleaner energy options.
“The Khurja power plant was feasible when first proposed 8 years ago in response to power supply shortages and outages across northern India, but technology and relative costs has moved on,” Buckley said.
Renewable energy generation in India is now cheaper than the proposed Khurja plant, with ongoing price declines prompting states, including Uttar Pradesh, to seek solar and wind options to meet incremental demand growth.
The Khurja non-minemouth coal proposal relies on a prohibitively expensive 900km long rail haul to bring coal to the plant, incurring significant freight charges, and increasing the cost of energy it produces. Additionally, the market price of coal continues to increase globally.
“A realistic tariff for Khurja is near Rs5.67/ kilowatt hour,” Buckley said. “When this is compared to clean renewable energy tariffs available +/- Rs3.00/kilowatt hour, the economics of the project look dim.”
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi is aiming to achieve 40% of its electricity generation needs by 2030 from non-fossil fuel sources including wind and solar.
Kashish Shah, IEEFA Energy Research Associate and co-author of the report, says India’s ambition to sustain 7-8% annual economic growth hinges on improving energy security and reducing the cost of power, and that requires sensible investment.
“Most of the state’s incremental electricity demand will be met by cheaper, cleaner renewable energy capacity and energy / grid efficiency gains over the next ten years, not through an overpriced, outdated, and uncompetitive monolith like the Khurja plant,” Shah said.
Like many other thermal power plants now in financial distress, Khurja will likely add to the lender, Power Finance Corporation’s US$4.5bn (Rs31,000 crore) of stranded assets, and has been doggedly hampered by numerous legal and environmental challenges still before the courts.
The report’s authors suggest diversifying into the non-minemouth coal-fired power sector is entirely outside TDHC’s core expertise and a high risk proposition no longer aligned with the Government of India’s energy sector plan.
“A pumped hydro storage project would far better align with India’s world leading electricity sector transformation,” Shah said. “India needs further investment in deflationary renewables, not more thermal power plants.”
Following careful analysis the report authors suggest it is unlikely the expensive Khurja plant will ever operate to capacity, and increasingly likely the financial sector will have to carry another stranded asset.
“Before any final decision to proceed with Khurja is made, the parties must carefully evaluate the project’s long-term financial viability and reassess India’s needs,” Buckley said.
“We recommend the long delayed, excessively expensive and redundant Khurja project be cancelled before it becomes another expensive stranded asset in India.”
Full report: The Khurja Thermal Power Project: A Recipe for an Indian Stranded Asset
END
Kate Finlayson – Sydney Australia +61 418 254 237
Tim Buckley – New Delhi India +61 408 102 127
Kashish Shah – New Delhi India +91 79 77 955 492
About IEEFA:
The Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) conducts global research and analyses on financial and economic issues related to energy and the environment.